News
A New Publication in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
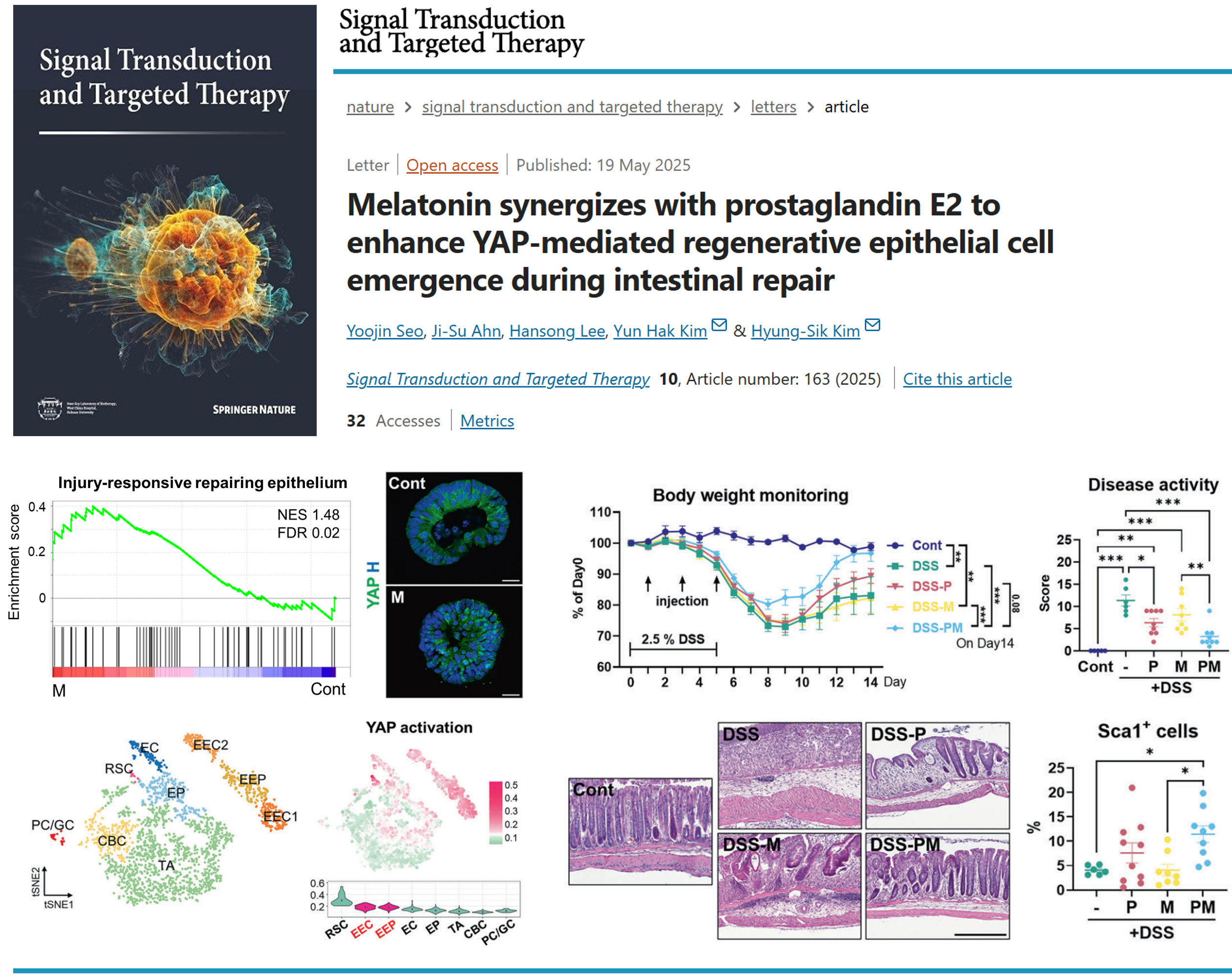
본 연구에서는 장 줄기세포 손상 이후 조직 재생을 유도하는 대체 경로로서, 상피세포 리프로그래밍(epithelial reprogramming)과 재건 줄기세포(revival stem cell, RSC)의 활성화에 주목하였습니다. 장 상피의 항상성을 유지하는 일반적인 줄기세포인 CBC(colonic crypt base columnar cell)는 외부 스트레스나 손상에 취약하여 쉽게 소실되며, 이때 손상 반응에 따라 RSC가 일시적으로 유도되어 손상된 줄기세포를 대체하고 조직 재건을 수행합니다. 본 연구에서는 멜라토닌이 장 상피세포의 가소성(plasticity)을 조절하고, 재생에 핵심적인 YAP신호를 강화함으로써 RSC 유도를 촉진할 수 있음을 규명하였습니다. 특히, 멜라토닌은 Prostaglandin E2(PGE2)와 병용 시 시너지 효과를 나타내어 RSC 유도를 유의미하게 향상시킵니다. 본 연구는 멜라토닌을 활용한 RSC 활성화 조절 가능성을 처음으로 제시하였으며, 이를 기반으로 다양한 장 손상 상황에 적용 가능한 새로운 재생 전략의 가능성을 보여주었습니다. 해당 논문은 2025년 5월 19일, Nature Publishing Group에서 발행하는 Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (IF=40.8, JCR 상위 0.96%)에 게재되었습니다.
This study focused on an alternative regenerative pathway activated following intestinal stem cell injury, highlighting epithelial reprogramming and the activation of revival stem cells (RSCs). Conventional intestinal stem cells, known as crypt base columnar (CBC) cells, are essential for maintaining epithelial homeostasis but are highly susceptible to external stress and damage. In response to injury, RSCs are transiently induced to replace lost stem cells and restore tissue integrity. We demonstrated that melatonin enhances RSC induction by modulating epithelial plasticity and reinforcing YAP signaling, a key pathway in intestinal regeneration. Notably, melatonin showed a synergistic effect when combined with prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), significantly enhancing RSC activation and regenerative responses. This study is the first to propose the regulatory potential of melatonin in RSC activation and suggests its application as a novel regenerative strategy for various intestinal injury conditions. The findings were published on May 19, 2025, in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (IF=40.8, JCR top 0.96%), a journal of Nature Publishing Group.